Energy Management explained
An Energy Management System (EMS), is a digital tool that monitors, analyzes, and documents energy consumption in buildings and facilities.
By collecting and analyzing data in real time, an EMS helps reduce energy waste, cut costs, and achieve sustainability goals—without compromising comfort or operational reliability.
Energy Management Made Simple
The purpose of an EMS is to provide a complete overview of energy use in buildings and facilities, while also identifying opportunities for efficiency and savings.
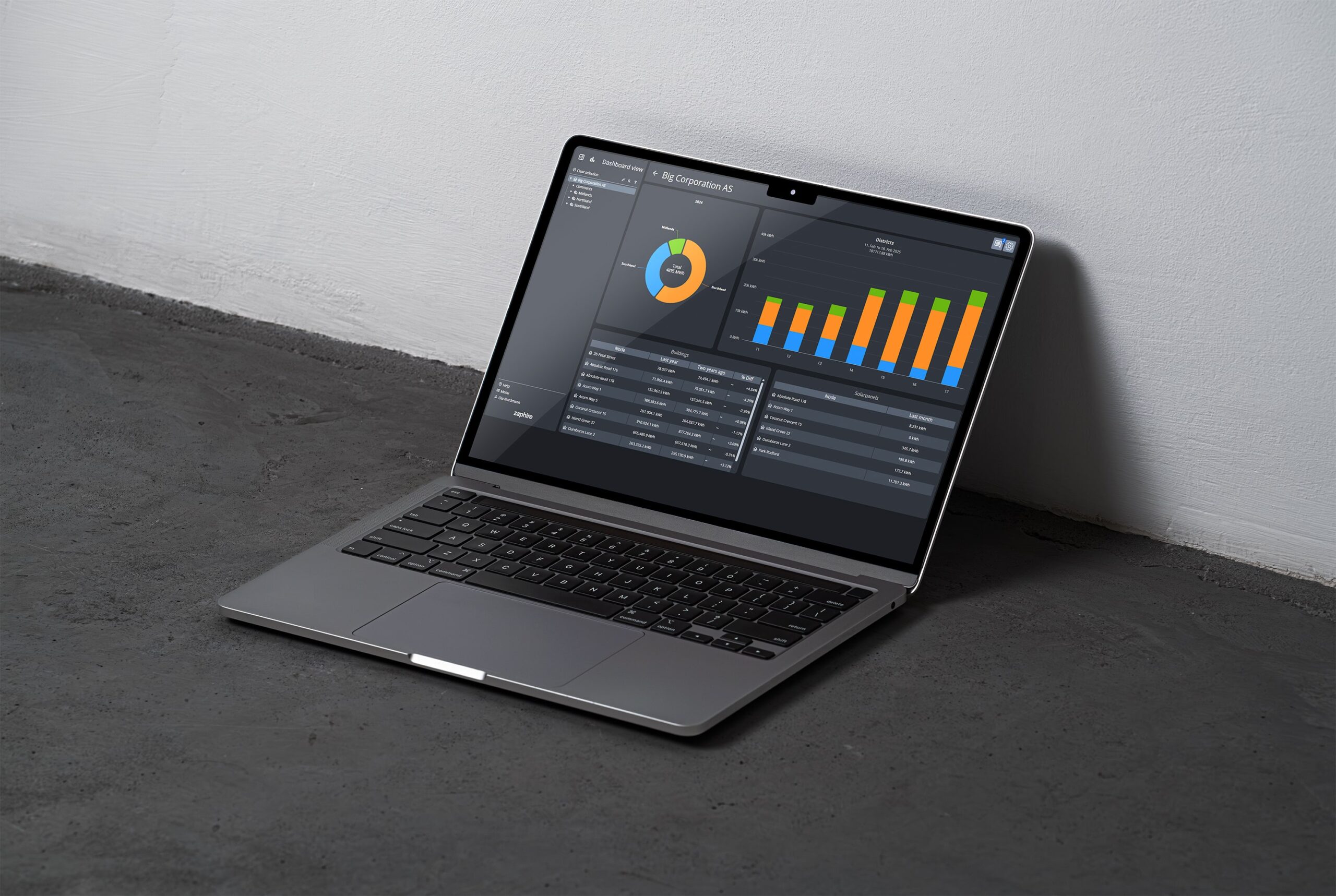
A modern EMS collects data from various energy sources and technical installations. The information is presented in real time through intuitive dashboards and reports, giving decision-makers a solid foundation to reduce costs, improve operations, and contribute to sustainability targets.
Users of the EMS system
An energy management system is relevant for a wide range of sectors and applications, and is today used by organizations that want better insight and control over their energy consumption.
In commercial buildings, such as office buildings, shopping centers, and hotels, the system ensures efficient operation of technical installations like ventilation, cooling, and lighting.
Schools and public buildings also benefit greatly from energy management, both to reduce operating costs and to meet public climate targets. For real estate companies, the system provides valuable insights into energy use across portfolios. These insights can be used for both optimization and documentation, for example in sustainability reporting and green financing. Municipalities and the public sector, such as Lillestrøm Municipality, are increasingly using energy management systems to gain better control of energy use in their own buildings. The system is also an important tool for achieving climate and energy goals in line with national and local strategies.
Combining Energy Management and Building Automation
When Energy Management is combined with a Building Management System (BMS), it becomes possible to monitor, control, and optimize energy consumption. In Zaphire BMS, adjustments can be made based on actual usage patterns, temperature, or other relevant data. This makes it easier to identify energy waste, adapt operations to building needs, and reduce both costs and environmental impact.
When Zaphire Top System (BMS) is integrated with Zaphire EMS, seamless interaction is achieved between operations and energy management. EMS provides detailed insights into consumption patterns, while the BMS handles control functions. Together, these systems enable EMS insights to directly regulate ventilation, heating, and lighting automatically.
Data-driven real-time optimization ensures that deviations or abnormal consumption are not only detected but can also trigger immediate actions in the BMS—for example, by adjusting operating times or temperatures.

How an Energy Management System Works
An Energy Management System acts as an intelligent link between technical installations and decision-makers. It collects, processes, and presents energy data in a way that enables understanding, analysis, and action—all in real time.
The foundation of an EMS is sensors and meters installed in buildings, production facilities, or technical installations. These devices continuously record data on electricity, heating, water, cooling, and other energy carriers.
In Zaphire, meters can be connected either via Zaphire IoT using BACnet or MODBUS TCP, or through third-party APIs that allow existing BMS/SCADA systems to keep meters updated. This makes it easy to integrate both new and existing meters into the same system. All information is securely transmitted and encrypted to Zaphire, where it is processed, structured, and made available through intuitive dashboards.
Data Visualization
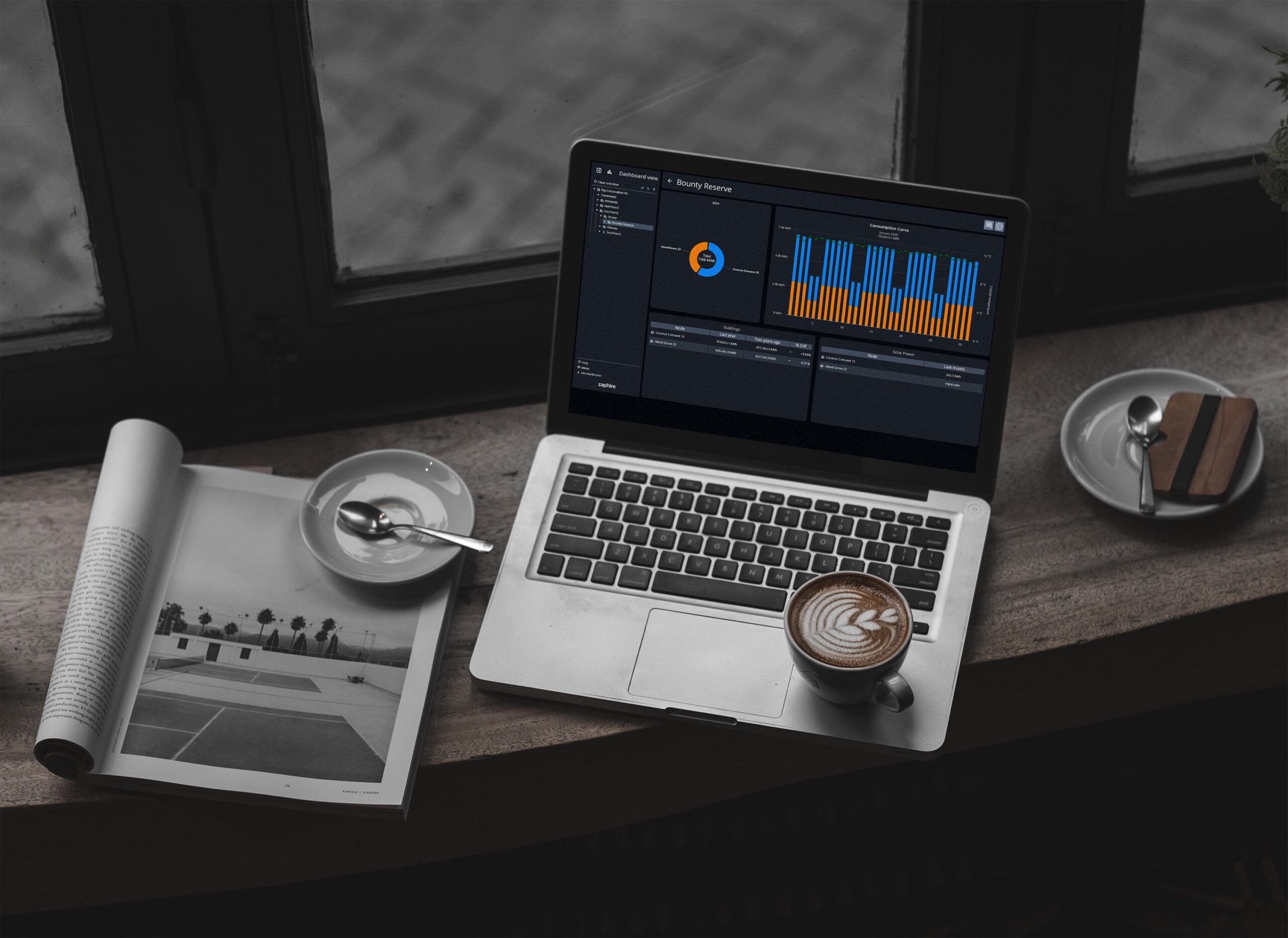
Energy data is visualized in user-friendly dashboards that provide insight into consumption patterns, trends, and deviations—both across buildings and down to detailed levels. Reporting tools make it easy to document energy use over time, which is valuable for both internal management and external reporting.
A modern EMS also makes it possible to automate and control building systems through integration with solutions such as the Zaphire Building Management System. This means the data is not only used for monitoring, but also for automatically optimizing operations—for example, by adjusting lighting, ventilation, or temperature based on actual needs and historical usage.
Zaphire Energy Management System
Discover how Zaphire’s cloud-based Energy Management System can transform your organization’s energy performance. With real-time insights and precise control over energy use, Zaphire EMS enables you to reduce costs while ensuring a healthy indoor climate.
The system is designed to be user-friendly and scalable, making it ideal for everything from commercial properties to industrial facilities.
Unlike traditional on-premise solutions, a cloud-based system provides real-time access and data-driven insights—anytime, anywhere, and from any internet-enabled device.

Key Features of Zaphire EMS
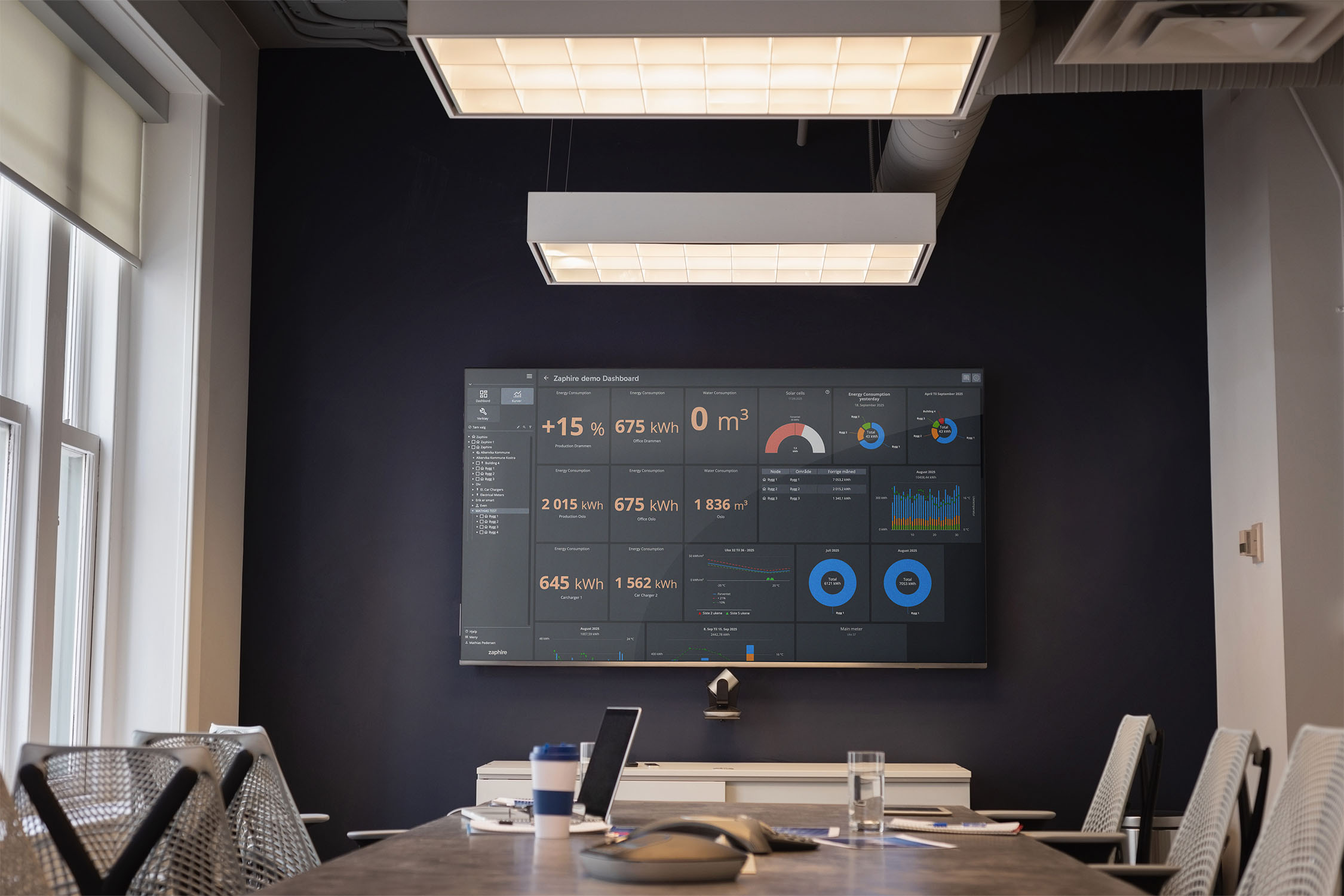
Zaphire EMS consists of several core features that together provide businesses with full control over their energy consumption. The system collects and processes large volumes of energy data, making the information accessible and easy to understand.
By combining real-time data with analytical tools and automated alerts, the system provides a complete picture of an organization’s energy use. In Zaphire, this includes:
Energy monitoring: Continuous data collection from meters, sensors, and systems for electricity, heating, cooling, temperature, and other energy carriers.
Energy analysis: Identify trends, consumption peaks, and anomalies. Use data-driven insights to optimize operations and reduce unnecessary energy use.
Alerts and reporting: Receive automatic notifications of abnormal consumption and generate reports for management, owners, or regulatory authorities.
Integration with building automation and production systems: The system can easily connect to existing solutions such as BMS, SCADA, or other technical platforms for seamless data collection and control.
Support for sustainability and energy savings: An EMS simplifies the process of setting and tracking energy targets, documenting climate impact, and complying with standards such as ISO 50001 or ESG reporting requirements.